Trigeminal Nerve Damage
Trigeminal Nerve Damage' title='Trigeminal Nerve Damage' />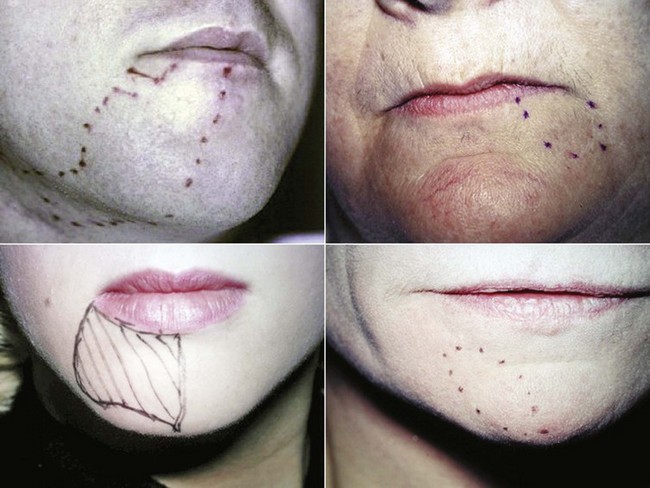
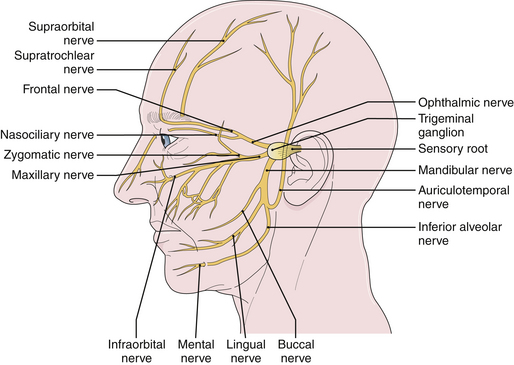 How to Alleviate Pain Caused by Trigeminal Neuralgia 1. Steps. Ask about surgery. History, causes, diagnoses, and more concerning the facial pain affliction known as Trigeminal Neuralgia courtesy of the Facial Pain Association. Trigeminal neuralgia is a progressive condition. Although medications can help you manage symptoms over time, more aggressive cases of this condition can lead to permanent damage to the trigeminal nerve, which can result in debilitating pain or partial permanent facial numbness. If you do not respond to medication surgery may be considered. Your doctor will work with you to help you choose the best surgery based on your health and medical background. The degree of severity of your trigeminal neuralgia, prior history of neuropathy, and general health all factor into the options that are available to you. The overall goal of surgery is to minimize damage to the trigeminal nerve as trigeminal neuralgia advances and to improve quality of life when medications no longer effectively manage pain. TRIGEMINAL NERVE NUCLEIThe sensory trigeminal nerve nuclei are the largest of the cranial nerve nuclei. The nucleus is divided into three parts, from rostral to caudal top to bottom in. The mesencephalic nucleus The chief sensory nucleus or pontine nucleus or main sensory nucleus or. The spinal trigeminal nucleus. The spinal trigeminal nucleus is further subdivided into three parts, from rostral. Pars Oralis Pars Interpolaris Pars Caudalis. There is also a distinct trigeminal motor nucleus that is medial to the chief sensory. The mesencephalic nucleus is involved with proprioception of the face, that is. TRIGEMINAL NERVE NUCLEI. The sensory trigeminal nerve nuclei are the largest of the cranial nerve nuclei, and extend through the whole of the midbrain, pons and. Images/nerves-surgery=damaged.jpg' alt='Trigeminal Nerve Damage' title='Trigeminal Nerve Damage' />Unlike many nuclei within the CNS, the mesencephalic. Instead, neurons. It is also the only structure in the CNS to contain the cell bodies. The principal sensory nucleus or chief sensory nucleus of V is a group of second. Pons. It receives information about discriminative sensation and light touch of the face. CN V. Most of the sensory information crosses the midline and travels to the contralateral. VPM of the thalamus via the Ventral trigeminothalamic tract. However, information of the oral cavity travels to the ipsilateral Ventral. Posteriomedial VPM of the thalamus via the Dorsal trigeminothalamic tract. The spinal trigeminal nucleus is a nucleus in the medulla that receives information. The facial. glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves also convey pain information from their areas. Motor branches of the trigeminal nerve. Motor branches of the trigeminal nerve are distributed in the mandibular nerve. These. fibers originate in the motor nucleus of the fifth nerve, which is located near the. Motor nerves are functionally quite different. In classical anatomy, the trigeminal nerve is said to have general somatic afferent. The. motor branches of the trigeminal nerve control the movement of eight muscles, including. Burke Hedges Books Pdf'>Burke Hedges Books Pdf. Muscles of mastication masseter temporalis medial pterygoid lateral pterygoid Other tensor veli palatini mylohyoid anterior belly of digastric tensor tympani. With the exception of tensor tympani, all of these muscles are involved in biting. All have bilateral cortical representation. A central lesion. However, injury to the peripheral nerve can cause paralysis of muscles on one side. Sccm 2012 Report Software Installed Collection. The jaw deviates to the paralyzed side when it opens. Somatotopic representation. Onion Skin Distribution of the Trigeminal Nerve. Exactly how paintemperature fibers from the face are distributed to the spinal trigeminal. The present understanding. Information. from the lower extremities is represented in the lumbar cord. Information from the. Information from the neck. Information from the. Within the spinal trigeminal nucleus, information is represented in an onion skin. The lowest levels of the nucleus in the upper cervical cord and lower medulla. Higher levels. in the upper medulla represent more central areas nose, cheeks, lips. The highest. levels in the pons represent the mouth, teeth, and pharyngeal cavity. The onion skin distribution is entirely different from the dermatome distribution. Lesions that destroy lower areas of. V1, upper lip V2 and mouth V3 while removing paintemperature. V1, cheeks V2 and chin V3. Analgesia in this distribution. Nevertheless, analgesia in exactly this distribution is found in humans after surgical. The spinal trigeminal nucleus sends paintemperature information to the thalamus. It also sends information to the mesencephalon and the reticular formation of the. The latter pathways are analogous to the spinomesencephalic and spinoreticular. The mesencephalon modulates painful input before it reaches. The reticular formation is responsible for the automatic. Wallenberg syndrome. Wallenberg syndrome also called the lateral medullary syndrome is a classic clinical. It provides a useful summary of. A stroke usually affects only one side of the body. If a stroke causes loss of sensation. The. only exceptions to this rule are certain spinal cord lesions and the medullary syndromes. Wallenberg syndrome is the most famous example. In Wallenberg syndrome. The explanation involves the anatomy of the brainstem. In the medulla, the ascending. A stroke that. cuts off the blood supply to this area e. The result is loss of paintemperature.
How to Alleviate Pain Caused by Trigeminal Neuralgia 1. Steps. Ask about surgery. History, causes, diagnoses, and more concerning the facial pain affliction known as Trigeminal Neuralgia courtesy of the Facial Pain Association. Trigeminal neuralgia is a progressive condition. Although medications can help you manage symptoms over time, more aggressive cases of this condition can lead to permanent damage to the trigeminal nerve, which can result in debilitating pain or partial permanent facial numbness. If you do not respond to medication surgery may be considered. Your doctor will work with you to help you choose the best surgery based on your health and medical background. The degree of severity of your trigeminal neuralgia, prior history of neuropathy, and general health all factor into the options that are available to you. The overall goal of surgery is to minimize damage to the trigeminal nerve as trigeminal neuralgia advances and to improve quality of life when medications no longer effectively manage pain. TRIGEMINAL NERVE NUCLEIThe sensory trigeminal nerve nuclei are the largest of the cranial nerve nuclei. The nucleus is divided into three parts, from rostral to caudal top to bottom in. The mesencephalic nucleus The chief sensory nucleus or pontine nucleus or main sensory nucleus or. The spinal trigeminal nucleus. The spinal trigeminal nucleus is further subdivided into three parts, from rostral. Pars Oralis Pars Interpolaris Pars Caudalis. There is also a distinct trigeminal motor nucleus that is medial to the chief sensory. The mesencephalic nucleus is involved with proprioception of the face, that is. TRIGEMINAL NERVE NUCLEI. The sensory trigeminal nerve nuclei are the largest of the cranial nerve nuclei, and extend through the whole of the midbrain, pons and. Images/nerves-surgery=damaged.jpg' alt='Trigeminal Nerve Damage' title='Trigeminal Nerve Damage' />Unlike many nuclei within the CNS, the mesencephalic. Instead, neurons. It is also the only structure in the CNS to contain the cell bodies. The principal sensory nucleus or chief sensory nucleus of V is a group of second. Pons. It receives information about discriminative sensation and light touch of the face. CN V. Most of the sensory information crosses the midline and travels to the contralateral. VPM of the thalamus via the Ventral trigeminothalamic tract. However, information of the oral cavity travels to the ipsilateral Ventral. Posteriomedial VPM of the thalamus via the Dorsal trigeminothalamic tract. The spinal trigeminal nucleus is a nucleus in the medulla that receives information. The facial. glossopharyngeal, and vagus nerves also convey pain information from their areas. Motor branches of the trigeminal nerve. Motor branches of the trigeminal nerve are distributed in the mandibular nerve. These. fibers originate in the motor nucleus of the fifth nerve, which is located near the. Motor nerves are functionally quite different. In classical anatomy, the trigeminal nerve is said to have general somatic afferent. The. motor branches of the trigeminal nerve control the movement of eight muscles, including. Burke Hedges Books Pdf'>Burke Hedges Books Pdf. Muscles of mastication masseter temporalis medial pterygoid lateral pterygoid Other tensor veli palatini mylohyoid anterior belly of digastric tensor tympani. With the exception of tensor tympani, all of these muscles are involved in biting. All have bilateral cortical representation. A central lesion. However, injury to the peripheral nerve can cause paralysis of muscles on one side. Sccm 2012 Report Software Installed Collection. The jaw deviates to the paralyzed side when it opens. Somatotopic representation. Onion Skin Distribution of the Trigeminal Nerve. Exactly how paintemperature fibers from the face are distributed to the spinal trigeminal. The present understanding. Information. from the lower extremities is represented in the lumbar cord. Information from the. Information from the neck. Information from the. Within the spinal trigeminal nucleus, information is represented in an onion skin. The lowest levels of the nucleus in the upper cervical cord and lower medulla. Higher levels. in the upper medulla represent more central areas nose, cheeks, lips. The highest. levels in the pons represent the mouth, teeth, and pharyngeal cavity. The onion skin distribution is entirely different from the dermatome distribution. Lesions that destroy lower areas of. V1, upper lip V2 and mouth V3 while removing paintemperature. V1, cheeks V2 and chin V3. Analgesia in this distribution. Nevertheless, analgesia in exactly this distribution is found in humans after surgical. The spinal trigeminal nucleus sends paintemperature information to the thalamus. It also sends information to the mesencephalon and the reticular formation of the. The latter pathways are analogous to the spinomesencephalic and spinoreticular. The mesencephalon modulates painful input before it reaches. The reticular formation is responsible for the automatic. Wallenberg syndrome. Wallenberg syndrome also called the lateral medullary syndrome is a classic clinical. It provides a useful summary of. A stroke usually affects only one side of the body. If a stroke causes loss of sensation. The. only exceptions to this rule are certain spinal cord lesions and the medullary syndromes. Wallenberg syndrome is the most famous example. In Wallenberg syndrome. The explanation involves the anatomy of the brainstem. In the medulla, the ascending. A stroke that. cuts off the blood supply to this area e. The result is loss of paintemperature.